
Estimated Reading Time: 12 minutes
With over 60,000 fire incidents recorded in India between January and October 2023 alone, the need for robust, technologically advanced fire safety systems has never been more critical. India’s adoption of IS/ISO 7240 as its national fire alarm standard, combined with the recent Fire Detection and Alarm Systems (Quality Control) Order 2025 that will mandate BIS certification for fire safety products, marks the most significant transformation in India’s fire safety landscape in decades.
This isn’t just a regulatory update—it’s a complete paradigm shift that positions India alongside global leaders in fire safety technology.

For over five decades, India’s fire alarm industry operated primarily under IS 2189. This standard was established in 1962 and last revised in 2008. While IS 2189 served its purpose during an era of conventional fire alarm systems, it struggled to keep pace with rapid technological advancements. Particularly in wireless communication, addressable systems, and AIoT (Artificial Intelligence + Internet of Things) integration.
IS/ISO 7240 represents a fundamental departure from this legacy approach. Rather than creating yet another India-specific standard, BIS has adopted the international ISO 7240 series “identical under single numbering.” This means India is implementing the exact same technical specifications used across Europe, North America, and other technologically advanced markets.
The ISO 7240 series is comprehensive. It consists of multiple parts that cover everything from system design and installation (Part 14) to specific component requirements. Most significantly for India’s technological future, ISO 7240-25 specifically addresses components using radio-frequency (RF) transmission paths —in other words, wireless fire alarm technology.
In a landmark move, the Government of India through the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has issued the Fire Detection and Alarm Systems (Quality Control) Order, 2025. This order mandates BIS certification for fire detection and alarm system components, including wireless devices covered under IS/ISO 7240-25.
The implementation is phased based on enterprise size:
| Enterprise Type | Compliance Deadline |
|---|---|
| General Enterprises | 6 months from notification |
| Small Enterprises | 9 months from notification |
| Micro Enterprises | 12 months from notification |
This regulatory framework ensures that only systems meeting rigorous international standards can be manufactured, sold, and installed in India. It effectively eliminates substandard products from the market while giving businesses adequate time to achieve compliance.
Pro Tip for Consultants: Start specifying IS/ISO 7240-compliant systems now. Projects commissioned after the compliance deadlines must use certified equipment—early specification avoids procurement delays.

Perhaps the most transformative aspect of India’s adoption of IS/ISO 7240 is Part 25. It establishes rigorous technical requirements for wireless fire alarm components. This inclusion represents official recognition that wireless technology is not just viable—it’s the future of fire safety systems.
ISO 7240-25 specifies detailed requirements for RF transmission paths in fire detection and alarm systems. Key areas include:
These specifications ensure that wireless components can deliver the same reliability as traditional wired systems, while offering unprecedented flexibility.
The advantages are particularly relevant to India’s diverse building landscape:
Installation Flexibility: Wireless systems eliminate the need for extensive cable runs through walls, ceilings, and conduits. In a country where buildings range from modern glass-and-steel complexes to century-old heritage structures, this flexibility is invaluable.
Retrofitting a historic property with traditional wired systems often requires destructive modifications. Wireless technology preserves architectural integrity while delivering modern safety.
Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Traditional addressable systems require significant investment in cable infrastructure and labor for installation. They also demand ongoing maintenance of physical connections. Wireless systems dramatically reduce these costs.
According to market research from Allied Market Research, the cost-effectiveness of wireless solutions is driving adoption across Asia-Pacific markets. The region is expected to dominate global fire alarm system growth.
Rapid Deployment: India’s construction sector is booming, particularly in smart cities and commercial real estate. Wireless systems can be installed and commissioned significantly faster than wired alternatives. This is critical when project timelines are tight and delays are expensive.
Scalability: Wireless addressable systems make it simple to add detection points, expand coverage, or reconfigure layouts as building uses change. This scalability is essential in India’s dynamic commercial and industrial sectors.
IS/ISO 7240-25 ensures these benefits come without compromising safety. The standard mandates rigorous environmental testing, including performance verification across temperature extremes. This is particularly relevant given India’s climate diversity, from sub-zero mountain regions to 45°C+ desert and coastal areas with 90% humidity.
Important for Fire Officers: When conducting acceptance testing, verify that wireless devices include environmental test certifications covering the temperature and humidity ranges relevant to your installation location.
The transition from IS 2189 to IS/ISO 7240 isn’t simply a matter of updating technical specifications. It represents a fundamental shift in how India approaches fire safety standardization.
IS 2189 was designed for an era of conventional fire alarm systems. In these systems, detectors operated on simple circuits with limited intelligence. While the standard was eventually updated to accommodate basic addressable systems, it lacked the granularity needed for modern technology.
Wireless systems, AIoT integration, and advanced detection algorithms existed in a grey area—possible to implement, but without clear standardization or certification pathways.
IS/ISO 7240 takes a component-based approach. Different parts address specific system elements:
This modularity allows the standard to evolve as technology advances. New parts can be added to address emerging innovations.
Critically, IS/ISO 7240 is technology-agnostic in its requirements but specific in its performance criteria. Rather than prescribing exactly how a system must be built, the standard defines what performance levels must be achieved. This approach encourages innovation while maintaining rigorous safety standards.
IS/ISO 7240-25 ensures these benefits come without compromising safety. The standard mandates rigorous environmental testing, including performance verification across temperature extremes. This is particularly relevant given India’s climate diversity, from sub-zero mountain regions to 45°C+ desert and coastal areas with 90% humidity.
By adopting ISO 7240 identically, India ensures that fire safety systems installed here meet the same standards as those in Europe, the Middle East, and other regions following EN 54 or ISO 7240. This alignment:
For MEP consultants working on multinational projects, this standardization simplifies design consistency across geographies.
IS/ISO 7240 compliance isn’t just about meeting today’s regulatory requirements. It’s about building fire safety infrastructure that remains relevant and effective for decades to come.
While conventional systems can only indicate that a fire has been detected somewhere on a circuit (often covering large areas), addressable systems pinpoint the exact location of the activated detector. This precision is mandated by IS/ISO 7240-14, which specifies that systems must provide clear indication of the zone or specific detector in alarm.
In a large commercial complex, hospital, or industrial facility, this difference is critical. Addressable systems enable:
Systems like NFire that combine addressable precision with wireless flexibility represent the optimal implementation of IS/ISO 7240 requirements. These systems deliver:
While IS/ISO 7240 doesn’t specifically mandate artificial intelligence or IoT features, the standard’s performance-based approach creates space for these innovations. Advanced wireless addressable systems can integrate:
Predictive analytics that identify potential issues before they trigger alarms. Environmental compensation that reduces false alarms by understanding normal conditions. Remote monitoring that enables 24/7 oversight from centralized control rooms. Building Management System (BMS) integration for comprehensive facility management.
These AIoT capabilities operate within IS/ISO 7240’s framework. They use the standard’s requirements as a safety baseline while delivering enhanced functionality above and beyond minimum compliance.
NFire wireless addressable fire alarm systems exemplify how modern technology meets IS/ISO 7240 requirements:
Part 14 Compliance (Design and Installation): NFire systems are designed according to ISO 7240-14 specifications for system architecture, loop design, and device placement. The system’s addressing capability provides clear zone and device identification as required by the standard.
Part 25 Compliance (Wireless Components): NFire wireless detectors and devices meet ISO 7240-25 requirements for RF transmission integrity. This includes signal strength monitoring, interference detection, and environmental performance verification across temperature and humidity ranges relevant to Indian conditions.
The flexibility enabled by IS/ISO 7240-compliant wireless addressable systems makes them ideal for India’s diverse building stock:
Heritage Properties: Wireless deployment preserves architectural integrity while delivering modern fire safety. Hotels, museums, and historic government buildings benefit from invisible protection.
Rapid Construction Projects: Smart city developments, industrial parks, and commercial complexes can be protected faster, keeping pace with aggressive construction timelines.
Retrofit Applications: Existing buildings requiring fire safety upgrades can implement modern addressable systems without the disruption of extensive cable installation work.
Industrial Facilities: Manufacturing plants, warehouses, and logistics centers benefit from scalable wireless systems that adapt as layouts change and operations evolve.
India’s adoption of IS/ISO 7240 and the forthcoming mandatory BIS certification under the Quality Control Order 2025 are already reshaping India’s fire alarm market in profound ways.
The phased implementation of mandatory BIS certification addresses a longstanding problem in India’s fire safety market. The proliferation of substandard products that technically complied with minimal requirements but failed to deliver reliable performance.
Once fully implemented, this regulatory framework will create a level playing field. All products must meet rigorous international standards.
For building owners, facility managers, and fire safety consultants, this standardization will simplify decision-making. Rather than attempting to evaluate competing claims about system performance, stakeholders will be able to rely on BIS certification as proof of compliance with globally recognized standards.
According to Future Market Insights , addressable fire alarm systems are projected to experience the highest growth rate in India’s fire safety market. This trend directly correlates with IS/ISO 7240’s emphasis on precision, reliability, and advanced functionality—characteristics that define addressable technology.
The wireless addressable segment is positioned for particularly strong growth. Allied Market Research projects the Asia-Pacific wireless fire detection system market will grow at a 7.2% compound annual growth rate through 2031. India represents a significant portion of this expansion.
IS/ISO 7240 compliance requires higher quality standards, more rigorous testing, and better components. For MEP consultants and architects, this shifts the specification conversation from “lowest bid” to “total cost of ownership over the system’s lifetime.”
When evaluating systems for clients, consider factors like:
Wireless addressable systems that meet IS/ISO 7240 often deliver superior long-term value despite potentially higher initial capital costs. This is a critical consideration when presenting options to building owners and facility managers.
For MEP consultants designing modern commercial and institutional buildings, fire alarm systems no longer operate in isolation. IS/ISO 7240-compliant systems integrate seamlessly with Building Management Systems (BMS). This enables comprehensive facility monitoring and automated emergency response protocols.
This integration is particularly critical in:
Fire safety must coordinate with HVAC controls (for smoke management), access control (for automated egress), lighting systems (for emergency illumination), and elevator controls (for fire service access).
When specifying systems, architects and MEP consultants should verify that proposed fire alarm systems provide standard communication protocols for BMS integration. This is a capability that wireless addressable systems inherently support through their network architecture.
For MEP consultants, architects, and fire officers, verifying IS/ISO 7240 compliance is becoming a critical professional responsibility. As the Quality Control Order implementation deadlines approach, design specifications should explicitly require BIS certification documentation for all system components.
Critical for Fire Officers: Safety officers and fire officers conducting acceptance testing should refuse to commission systems lacking proper BIS certification once the mandatory compliance deadlines take effect. This professional stance protects both the building occupants and the approving officer from liability associated with substandard systems.
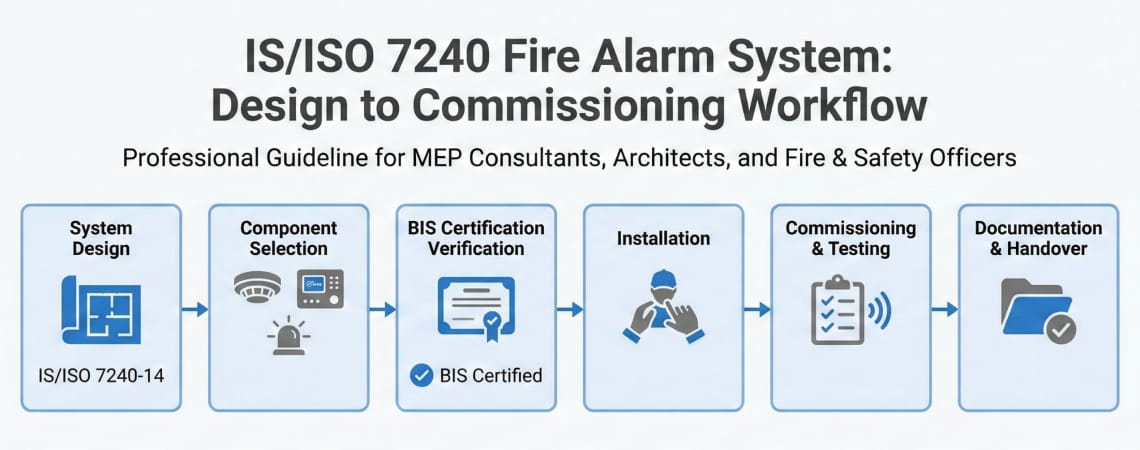
IS/ISO 7240 adoption creates both opportunities and responsibilities for MEP consultants, architects, safety officers, and fire officers. Understanding how to leverage this standard effectively is crucial for delivering compliant, future-proof fire safety solutions.
When specifying fire alarm systems under the IS/ISO 7240 framework, design professionals should verify several key aspects.
Ensure each system component carries appropriate IS/ISO 7240 part certification. This includes:
For wireless systems, specifically verify IS/ISO 7240-25 compliance.
Request detailed documentation showing how components meet ISO 7240-13 compatibility requirements. This ensures different system elements will communicate reliably. It also confirms components can be serviced or upgraded independently.
Given India’s climate diversity, verify that wireless components have been tested across the temperature and humidity ranges specified in ISO 7240-25. This is particularly critical for installations in extreme environments:
MEP consultants designing fire alarm systems under IS/ISO 7240 should consider several practical factors.
While wireless systems eliminate cable runs, proper RF design is critical. Conduct site surveys to identify:
ISO 7240-25 compliance ensures devices can handle interference. However, good design practice minimizes challenges from the outset.
Plan for easy access during battery replacement cycles.
Wireless detectors still require power, typically from batteries. Design considerations include:
Document the system’s expansion capacity. This value proposition often justifies higher initial investment to building owners.
One advantage of addressable wireless systems is ease of expansion. When designing systems, consider:
Specify standard communication protocols (BACnet, Modbus, etc.) to ensure interoperability.
Ensure specified systems can integrate with:
Safety officers and fire officers responsible for system acceptance must understand IS/ISO 7240 testing requirements.
Ensure reliable signal transmission under various conditions before final acceptance.
Wireless systems add an additional layer:
ISO 7240-14 specifies testing procedures for system commissioning. Unlike conventional systems where zones are tested as groups, addressable systems require individual device verification.
Proper commissioning under IS/ISO 7240 requires comprehensive documentation:
This documentation becomes critical during future maintenance, modifications, and annual testing cycles.
All tracked through the system’s monitoring capabilities and documented for regulatory compliance.
The standard establishes ongoing testing frequencies and procedures. For wireless systems, this includes:
Architects and MEP consultants working on retrofit projects face unique challenges that IS/ISO 7240-compliant wireless systems specifically address.
Heritage buildings, occupied facilities, and structures with difficult-to-access spaces benefit enormously from wireless technology. Benefits include:
Wireless addressable systems enable phased installations. Sections of a building can be upgraded systematically without compromising the entire fire safety infrastructure. This is particularly valuable in:
When retrofitting, verify that the complete system—not just new components—meets current IS/ISO 7240 requirements. This may require:
IS/ISO 7240 adoption demands updated professional knowledge. Fire officers and safety officers should invest in:
Move beyond conventional zone-based thinking to device-level monitoring and control. Learn how addressing schemes work, how devices communicate, and how to troubleshoot individual device issues.
These are skills that weren’t necessary with traditional wired systems but are now essential.
Understand RF communication principles relevant to fire alarm systems:
ISO 7240 is a living standard. Parts are added as technology evolves. Professional development should include:
Continuous learning ensures you remain competent with evolving technology and requirements.
IS/ISO 7240 is India’s adopted international standard for fire detection and alarm systems. BIS adopted the ISO 7240 series “identical under single numbering,” meaning India uses the exact same specifications as international markets. The standard covers all aspects of fire alarm systems, from system design to individual component requirements.
The Fire Detection and Alarm Systems (Quality Control) Order 2025 makes BIS certification under IS/ISO 7240 mandatory. Implementation is phased based on enterprise size: 6 months for general enterprises, 9 months for small enterprises, and 12 months for micro enterprises from the notification date.
ISO 7240-25 specifically addresses components using radio-frequency (RF) transmission paths. This part establishes rigorous requirements for wireless fire alarm components, including transmission integrity, signal stability, interference resistance, and environmental performance. This official recognition makes wireless technology a fully standardized, compliant approach for fire alarm systems in India.
IS 2189 was India’s legacy standard, last revised in 2008, designed primarily for conventional and basic addressable wired systems. IS/ISO 7240 is a comprehensive international standard that explicitly supports wireless technology, provides component-level specifications, enables global compatibility, and follows a performance-based approach that encourages innovation while maintaining safety standards.
Existing systems installed under IS 2189 are typically grandfathered and don’t require immediate upgrade. However, new installations and major system modifications should comply with IS/ISO 7240. Additionally, when existing systems reach end-of-life or require significant repairs, upgrading to IS/ISO 7240-compliant systems is recommended to ensure long-term supportability and parts availability.
BIS certification verifies that fire alarm system components meet all technical requirements specified in relevant IS/ISO 7240 parts. This includes performance testing, environmental testing, reliability verification, and compatibility assessment. For wireless components, certification specifically confirms ISO 7240-25 compliance for RF transmission reliability.
When compliant with IS/ISO 7240-25, wireless addressable systems deliver equivalent reliability to wired systems. The standard mandates rigorous testing for signal integrity, interference resistance, and environmental performance. Wireless systems include continuous monitoring that alerts if communication paths are compromised, often detecting issues faster than periodic testing of wired connections might.
ISO 7240-13 addresses compatibility and interconnectability of system components. While complete cross-manufacturer compatibility isn’t guaranteed, the standard’s component-level approach and compatibility assessment requirements make it more feasible than under previous standards. Always verify compatibility with manufacturers and conduct integration testing during commissioning.
India’s transition from IS 2189 to IS/ISO 7240 fundamentally changes how fire safety professionals approach system design, specification, and implementation. By adopting international standards identical to those used globally, India ensures that buildings across the country benefit from cutting-edge fire protection technology. This technology is backed by rigorous testing and proven performance.
For MEP consultants and architects, the standard’s explicit provisions for wireless technology in ISO 7240-25 create new design possibilities. These were combined with its performance-based approach to addressable systems. Systems that were once considered premium options are now part of the standardized mainstream. They offer installation flexibility and long-term value that can be confidently specified for projects ranging from heritage retrofits to smart city developments.
Once fully implemented, this regulatory framework will create a level playing field. All products must meet rigorous international standards.
For building owners, facility managers, and fire safety consultants, this standardization will simplify decision-making. Rather than attempting to evaluate competing claims about system performance, stakeholders will be able to rely on BIS certification as proof of compliance with globally recognized standards.
For safety officers and fire officers, IS/ISO 7240 provides clear compliance benchmarks and testing protocols. These ensure systems perform reliably throughout their operational life. Understanding addressable and wireless technology is no longer optional—it’s a core professional competency.
The Quality Control Order 2025’s phased implementation gives the industry time to adapt. But the direction is clear. Wireless addressable systems meeting IS/ISO 7240 aren’t just meeting regulatory requirements—they’re delivering infrastructure that will remain relevant, supportable, and effective for decades.
As design professionals, specifying systems that embrace these technologies isn’t about chasing trends. It’s about providing clients with solutions aligned with India’s fire safety future.
IS/ISO 7240 adoption aligns India with global fire safety standards , giving design professionals confidence that specified systems meet internationally recognized performance criteria
ISO 7240-25 provides comprehensive specifications for wireless fire alarm components, enabling MEP consultants and architects to confidently specify wireless addressable systems for projects ranging from heritage retrofits to new construction
The Fire Detection and Alarm Systems (Quality Control) Order 2025 establishes phased BIS certification requirements (6-12 months based on enterprise size), giving professionals clear timelines for when compliance verification becomes mandatory
Addressable wireless systems deliver IS/ISO 7240 compliance while solving practical design challenges: installation flexibility, reduced infrastructure costs, retrofit-friendly deployment, and easy scalability for future modifications
Component-level compliance verification is essential : Safety officers and fire officers must verify that each system element carries appropriate IS/ISO 7240 part certification, particularly ISO 7240-25 for wireless components
Commissioning requirements under IS/ISO 7240 are more rigorous than previous standards, requiring device-level testing, comprehensive documentation, and wireless link quality verification for RF-based systems
Professional competency in addressable and wireless technology is now essential for fire officers and safety officers responsible for system acceptance, testing, and ongoing maintenance
Retrofit projects benefit enormously from wireless technology specified under IS/ISO 7240-25, enabling fire safety upgrades without destructive building modifications
Total cost of ownership analysis justifies quality specifications: When MEP consultants and architects present wireless addressable systems to clients, long-term maintenance savings, scalability, and reliability often outweigh higher initial costs