A Technology-Driven Approach to Industrial Safety in India and Beyond

In February 2024, a devastating fire at a chemical processing facility in Gujarat resulted in twelve fatalities and caused damages exceeding ₹300 crore. The incident investigation revealed a sobering truth: the catastrophic failure could have been prevented. Temperature sensors had detected anomalous readings four hours before the explosion, but without predictive analytics to interpret these signals as precursors to disaster, the warnings went unheeded. This tragedy exemplifies a critical gap in traditional fire safety approaches—the inability to recognize and act upon incipient hazards before they escalate.
According to the National Crime Records Bureau, India experienced over 1.4 lakh fire incidents in 2023, with industrial fires accounting for approximately 12% of these cases. The direct economic impact exceeded ₹2,800 crore, while indirect costs—including business interruption, supply chain disruption, and reputational damage—multiplied this figure several times over. More critically, these incidents claimed hundreds of lives and injured thousands more.
Traditional reactive approaches to fire safety—waiting for smoke detectors to trigger or conducting periodic manual inspections—are no longer adequate for India’s rapidly industrializing landscape. The transition from reactive to proactive safety requires a fundamental paradigm shift, one powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based predictive maintenance (PdM). This technology doesn’t just detect fires; it prevents them by identifying subtle anomalies that precede catastrophic failures, often days or weeks before disaster strikes.
Recent Hotel Fire Tragedies in India:
Predictive maintenance represents the evolution of industrial safety from reactive crisis management to proactive risk mitigation. Unlike traditional preventive maintenance, which follows fixed schedules regardless of actual equipment condition, PdM uses real-time data and advanced analytics to predict when failures are likely to occur.

Reactive Maintenance: Traditional “run-to-failure” approach where equipment is repaired only after breaking down. In fire safety, this means responding to incidents after they occur—often with devastating consequences.
Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled inspections and replacements based on time intervals or usage metrics. While an improvement, this approach often leads to unnecessary maintenance or misses developing issues between scheduled checks.
Predictive Maintenance: Condition-based monitoring using AI, machine learning (ML), and Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) sensors to predict failures before they occur. This approach optimizes maintenance timing, reduces costs, and—most critically for fire safety—prevents catastrophic incidents.
Modern predictive maintenance for fire safety leverages an integrated AIoT (Artificial Intelligence + Internet of Things) technology stack that combines multiple layers:
This integrated approach complies with both Indian (IS/ISO 7240) and European (EN54) standards, ensuring that predictive capabilities are built on a foundation of proven fire safety protocols. Advanced wireless addressable systems—such as the NFire AIoT platform developed in India—demonstrate how modern technology can enhance, rather than replace, traditional fire safety requirements while delivering predictive intelligence that transforms risk management.
The most valuable contribution of AI-based predictive maintenance is its ability to identify “incipient” defects—subtle anomalies that precede major failures. In industrial environments, particularly chemical processing and manufacturing, the transition from initial fault to full-scale fire or explosion can occur in mere seconds. This compressed timeline makes early detection not just beneficial, but absolutely critical.
Incipient hazards are pre-ignition indicators that traditional detection systems often miss. These include:
Traditional fire alarm systems are designed to detect smoke, heat, or flames—all signs that a fire has already begun. AI-driven anomaly detection platforms, by contrast, continuously scan multi-sensor data streams to flag deviations that may indicate a fire is about to start. A temperature sensor showing a 2°C increase over baseline might seem insignificant in isolation, but when an AIoT system like NFire correlates it with increased particulate levels and declining air pressure, it becomes a critical early warning that can save lives and prevent catastrophic losses.
In November 2023, a pharmaceutical warehouse in Pune equipped with an AI-powered wireless addressable fire system detected unusual thermal patterns in its cold storage section. Temperature sensors registered gradual warming over 36 hours—from the required -20°C to -15°C—while humidity sensors detected moisture accumulation. The AI system correlated these readings and predicted a compressor failure that would lead to thermal runaway in refrigerated chemical storage within 48 hours. Maintenance teams intervened, replacing the failing compressor and preventing what could have been a catastrophic release of reactive materials. Post-incident analysis confirmed that without this early warning, the failure would have occurred during weekend operations when minimal staff were present, with potentially devastating consequences.
See how NFire’s AIoT platform can identify fire risks before they become emergencies.
Predictive maintenance systems deploy specialized sensor technologies, each addressing specific catastrophic failure modes. Unlike conventional single-point detection, AIoT platforms integrate multiple sensor types to create a comprehensive safety net.
Technology: Thermal imaging cameras and distributed temperature sensing (DTS) using fiber optic cables provide continuous 24/7 monitoring across large areas.
Application: Critical for detecting hotspots in electrical distribution panels, conveyor belt systems, bulk material storage, and process equipment before visible smoke or flames appear.
Preventive Value: Identifies ignition sources hours or days before combustion occurs. Particularly effective for preventing spontaneous combustion in coal storage, grain silos, and textile warehouses where internal heating can smolder undetected.
Indian Context: A Mumbai textile manufacturing facility using fiber optic temperature monitoring detected internal heating in a cotton bale storage area 72 hours before critical temperature was reached. The early warning allowed controlled ventilation and moisture treatment, preventing what fire investigators estimated would have been a ₹50 crore loss event.
Technology: Ultrasonic sensors detect high-frequency sound waves (typically 20-100 kHz) generated by turbulent gas flow in pressurized systems.
Application: Identifies leaks of flammable gases (LPG, natural gas, hydrogen) or toxic compounds (ammonia, chlorine) in industrial facilities, regardless of wind direction or gas dilution.
Preventive Value: Provides instantaneous detection of leaks that could form explosive clouds or create toxic exposure hazards. Unlike traditional gas sensors that require molecules to reach the detector, acoustic sensors identify leaks at the source.
Example: A chemical processing plant in Gujarat implemented ultrasonic leak detection across its ammonia refrigeration system. Within the first month, the system detected three micro-leaks in valve seals and pipe joints that conventional sensors had missed. Each leak, while small, represented a potential explosion hazard in the confined equipment room.
Technology: Continuous vibration monitoring using accelerometers on rotating machinery (pumps, compressors, motors, fans) detects mechanical degradation through waveform analysis.
Application: Identifies bearing wear, shaft misalignment, rotor imbalance, and loosened components before catastrophic failure occurs.
Fire Prevention Link: Mechanical failures in process equipment can generate friction sparks, cause loss of containment in flammable fluid systems, or lead to motor overheating and electrical fires.
AI Enhancement: Machine learning algorithms analyze vibration waveforms to predict how quickly a defect is progressing, enabling risk-based prioritization of repairs. A bearing showing 15% degradation on a non-critical pump might be scheduled for next maintenance cycle, while the same degradation on a flammable liquid transfer pump triggers immediate intervention.
The true power of AIoT platforms emerges when multiple sensor types are integrated. Modern wireless addressable fire systems like NFire can combine smoke detection, heat sensing, gas monitoring, and environmental parameters (humidity, air pressure, wind direction, wind velocity) to create comprehensive situational awareness. For example, a thermal sensor detecting rising temperature near a conveyor belt, combined with smoke particle detection and vibration anomalies from the drive motor, provides far higher confidence of an incipient fire than any single indicator alone. This multi-criteria approach dramatically reduces false alarms while improving early detection accuracy—a critical requirement for compliance with IS/ISO 7240 standards and the upcoming NBC 2025 mandates.
One of the most catastrophic consequences of industrial fires is the “domino effect”—where a primary incident triggers secondary events in adjacent equipment or facilities, creating exponentially severe outcomes. The 1984 Bhopal gas tragedy, India’s worst industrial disaster, exemplified this cascade failure mechanism: a water ingress into a storage tank triggered an exothermic reaction, which led to pressure buildup, rupture, and toxic gas release affecting thousands.
Industrial facilities often contain multiple hazardous processes in close proximity. A fire or explosion in one unit can:
The 2020 Visakhapatnam styrene gas leak, while primarily a chemical release, demonstrated domino effects: the initial leak caused polymer formation blocking safety valves, which increased pressure, causing further leaks, and created a toxic cloud affecting surrounding residential areas.
The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA) Process Safety Management (PSM) standard identifies “mechanical integrity” as a core element of preventing catastrophic releases. Mechanical integrity means ensuring that process equipment—pumps, valves, pressure vessels, piping systems—is designed, installed, operated, and maintained to prevent failures.
This is precisely where predictive maintenance delivers its greatest value in domino effect prevention. By identifying and resolving minor issues—a failing pump seal, a corroded pipe section, an overheating motor bearing—before they progress to catastrophic failure, PdM systems break the accident sequence that would otherwise cascade through a facility.
Scenario: A petrochemical facility stores flammable liquid in multiple interconnected tanks. A pump seal begins degrading due to chemical exposure and mechanical wear.
Without Predictive Maintenance:
With AI-Based Predictive Maintenance:
The economic disparity is striking: a ₹50,000 investment in proactive repair prevents a ₹200 crore disaster—an ROI exceeding 400,000%. More importantly, it saves lives.
The business case for AI-based predictive maintenance in fire safety extends beyond preventing catastrophic losses. Quantifiable benefits span multiple operational and financial dimensions, making PdM not just a safety imperative but a sound business investment.
Research from McKinsey & Company and multiple industry studies consistently demonstrates that predictive maintenance reduces overall maintenance costs by 18-25% compared to reactive approaches. This savings comes from:
Downtime Reduction: 30-50%
Unplanned downtime costs Indian manufacturers an estimated ₹1,200-1,500 per minute according to industry surveys. AI-powered PdM systems reduce equipment breakdowns by approximately 50%, translating directly to production continuity. For a medium-sized manufacturing facility experiencing 100 hours of unplanned downtime annually, this represents ₹72-90 lakh in recovered production value.
False Alarm Reduction: Up to 90%
Traditional fire detection systems suffer from false alarm rates that can reach 30-40% in industrial environments with dust, steam, or temperature fluctuations. Each false alarm triggers evacuation, production stoppage, and emergency response mobilization—conservatively costing ₹50,000-2,00,000 per incident. AI-based multi-criteria detection reduces false alarms by up to 90% through intelligent correlation of sensor data, eliminating alerts caused by cooking fumes, steam, dust, or sensor drift.
Insurance Premium Reductions: 10-20%
Leading commercial property insurers in India increasingly recognize the risk reduction value of predictive maintenance and advanced fire safety systems. Facilities demonstrating comprehensive AIoT-based monitoring, particularly those compliant with IS/ISO 7240 and EN54 standards, qualify for premium reductions ranging from 10-20%. For a large industrial facility with annual premiums of ₹50 lakh, this represents ₹5-10 lakh in annual savings.
Business Continuity Protection:
The Allianz Risk Barometer 2024 identifies business interruption as the top global business risk, driven by interconnected supply chains and just-in-time manufacturing. A catastrophic fire doesn’t just destroy physical assets—it can trigger supply chain collapse, customer contract penalties, regulatory scrutiny, and reputational damage that extends far beyond immediate repair costs. Predictive maintenance protects the “license to operate” by demonstrating corporate responsibility and regulatory compliance.
Industry data compiled from implementations across manufacturing, chemical processing, and warehouse facilities shows:
Example: A pharmaceutical manufacturing facility in Hyderabad invested ₹45 lakh in a comprehensive wireless addressable AIoT fire safety system with predictive maintenance capabilities. First-year quantifiable benefits included: ₹8.2 lakh in reduced maintenance costs, ₹12.5 lakh in eliminated false alarm disruptions, ₹6.8 lakh in insurance premium reduction, and ₹18 lakh in prevented downtime from early equipment failure detection. Total first-year return: ₹45.5 lakh—achieving payback in 11.9 months.
Deploying AI-based predictive maintenance for fire safety requires strategic planning, but modern wireless addressable systems have dramatically simplified implementation compared to traditional wired installations.
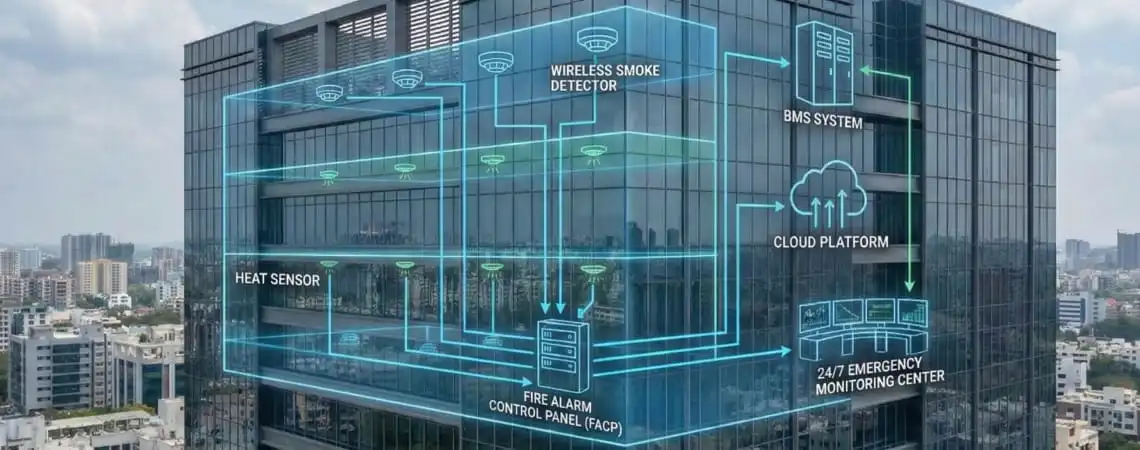
One of the primary concerns facility managers express is compatibility with existing fire safety and building management systems. Modern AIoT platforms like NFire address this through open protocols:
Wireless addressable technology offers particular advantages for retrofitting existing facilities. Unlike conventional wired systems requiring extensive conduit installation, cable pulling, and structural modifications, wireless sensors can be deployed in hours rather than weeks. NFire’s 100% wireless addressable architecture, for instance, reduces installation time from days or weeks to mere hours, dramatically lowering deployment costs—often by 40-60%—and eliminating production disruption during installation.
IS/ISO 7240 Compliance:
The IS/ISO 7240 series represents India’s primary fire detection and alarm system standards, adopted from international ISO specifications. These standards specify requirements for fire detection, alarm systems, control panels, power supplies, and system design. Any AIoT platform deployed in India must demonstrate compliance with relevant IS/ISO 7240 parts, including:
EN54 European Standard:
EN54 provides additional assurance of international quality and interoperability. Systems certified to both IS/ISO 7240 and EN54—like NFire—demonstrate dual compliance that facilitates exports, multinational facility standardization, and meets the highest global benchmarks. This dual certification positions Indian-developed platforms for both domestic and international markets while ensuring facilities receive world-class fire protection.
National Building Code 2025 Updates:
India’s National Building Code 2025 introduces stricter fire safety requirements, including mandatory addressable systems for larger facilities, enhanced monitoring capabilities, and integration with building automation. Systems like NFire are designed to be “NBC 2025 Ready,” meaning facilities installing these platforms today are future-proofed against upcoming regulatory changes. This forward compatibility protects capital investments and eliminates the need for costly retrofits when new regulations take effect.
IoT-connected systems introduce cybersecurity concerns that must be addressed through defense-in-depth strategies:
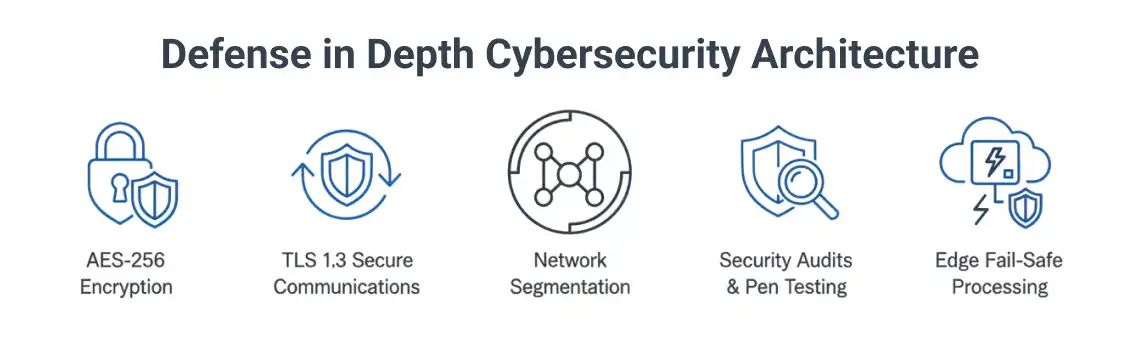
Leading wireless addressable platforms like NFire incorporate these security measures from the ground up—including AES-256 encryption and TLS 1.3 protocols—ensuring that connectivity enhancements don’t create new vulnerabilities. The system remains fully functional for local fire detection even if internet connectivity is lost, with cloud features enhancing rather than replacing core safety functions.
India’s industrial landscape presents both unique challenges and extraordinary opportunities for AI-based predictive maintenance in fire safety.
India’s fire protection market is experiencing rapid growth driven by multiple factors:
Market research indicates the Indian fire safety systems market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8-10% through 2030, with wireless and intelligent systems representing the fastest-growing segments.
Environmental Extremes:
India’s climate poses specific challenges for fire detection systems. Summer temperatures exceeding 45°C in northern regions, humidity levels above 90% during monsoons, and dust-heavy environments in industrial zones stress conventional detection technology. Early Indian fire safety efforts often relied on imported sensors designed for temperate climates, leading to false alarms and reliability issues. This challenge drove indigenous R&D—notably through partnerships between industry and institutions like IIT Gandhinagar—to develop sensors and algorithms specifically engineered for Indian environmental conditions. Platforms like NFire, developed through such collaborations, incorporate environmental compensation algorithms that maintain accuracy across India’s extreme climate variations.
Heterogeneous Infrastructure:
Indian industrial facilities often combine modern and legacy equipment, creating integration challenges. A pharmaceutical plant might feature cutting-edge production lines alongside decades-old HVAC systems. Wireless addressable systems excel in these environments by eliminating the need to run cables through existing structures while maintaining compatibility through open protocols. NFire’s support for Modbus, BACnet/IP, and TCP/IP enables seamless integration with both legacy and modern building systems.
Cost Sensitivity:
While large corporations increasingly adopt advanced fire safety technology, mid-size enterprises often struggle with upfront costs. This is where the business case for predictive maintenance becomes critical—demonstrating rapid ROI through reduced insurance premiums, prevented downtime, and maintenance savings makes the investment financially accessible. Additionally, wireless installation cost advantages (40-60% lower than wired systems) reduce barriers to entry.
Indian Railways Implementation:
Indian Railways, managing thousands of stations and maintenance facilities nationwide, has progressively adopted wireless addressable fire systems for modernization projects. The wireless deployment advantage proves particularly valuable in heritage stations where running cables would compromise architectural integrity. Predictive maintenance capabilities enable centralized monitoring across dispersed locations, with AI algorithms identifying equipment degradation patterns before failures occur.
Critical Infrastructure Protection:
From India Post sorting facilities to State Bank of India data centers, AIoT-based fire safety systems like NFire protect critical national infrastructure. These implementations demonstrate how predictive analytics can ensure 24/7 protection for assets that cannot afford even minutes of downtime. The NFire Connect mobile app enables rapid response even outside business hours, while cloud-based Command Centre dashboards provide visibility to corporate safety teams and regulatory authorities.
Manufacturing Excellence:
Leading Indian manufacturing companies—from Aditya Birla Group facilities to automotive component manufacturers—have integrated predictive fire safety into their Industry 4.0 strategies. These implementations combine fire detection with broader equipment health monitoring, creating comprehensive asset protection programs that simultaneously improve safety and operational efficiency. NFire installations across pharma manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics demonstrate the platform’s versatility across diverse industrial applications.
Transitioning to smart fire safety doesn’t have to be complex. Our experts can help you map out a future-ready transition plan that balances world-class safety with your current infrastructure.
The evolution of AI-based predictive maintenance continues to accelerate, with emerging technologies promising even greater capabilities in catastrophic failure prevention.
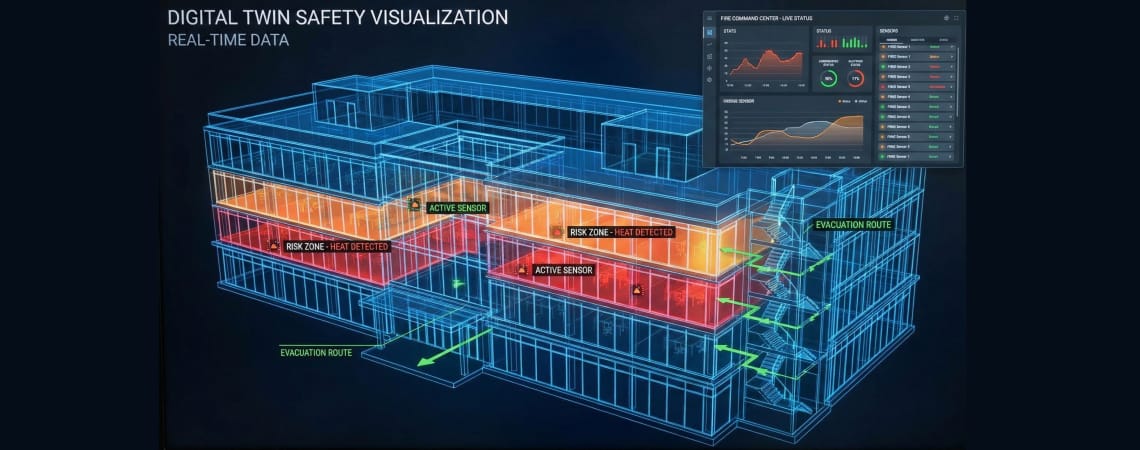
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical facilities—represent the next frontier in predictive fire safety. These sophisticated models:
Advanced AIoT platforms like NFire are already incorporating 2D and 3D digital twin visualization through their Command Centre interface, enabling facility managers to “see” their facilities’ fire risk profile in real-time. During an incident, these visualizations guide emergency responders to the precise location and provide situational awareness about surrounding hazards, evacuation routes, and optimal suppression strategies.
The next generation of predictive maintenance systems will increasingly diagnose their own health:
This self-awareness reduces the maintenance burden on facility teams while ensuring that the protective system itself never becomes a single point of failure.
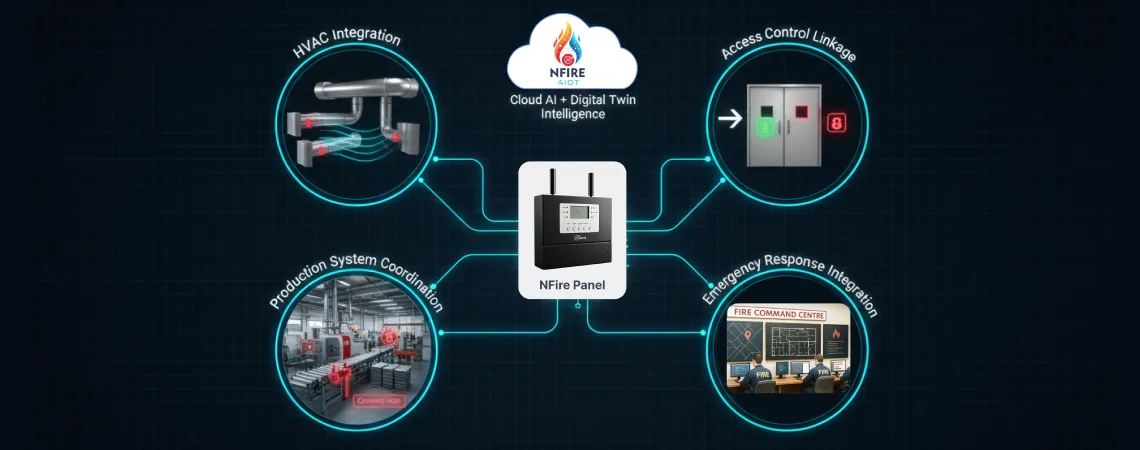
Fire safety systems are evolving from standalone protective equipment to integral components of intelligent facilities:
These integrations transform fire safety from an isolated system into a coordinated facility-wide response capability, dramatically improving both prevention and mitigation outcomes. NFire’s ecosystem—spanning fire alarm panels (N7, N70, N700, N707), multi-sensor devices, the Command Centre monitoring platform, and Connect mobile app—exemplifies this integrated approach.
Research continues to expand the sensor technologies available for incipient fire detection:
The global AI video analytics market alone is projected to grow from $32 billion in 2025 to $133 billion by 2030, indicating massive investment in these intelligent sensing technologies.
The fundamental premise of AI-based predictive maintenance in fire safety is deceptively simple: prevent catastrophic failures by identifying and resolving issues before they escalate. Yet the impact of this paradigm shift extends far beyond preventing individual incidents.
Predictive maintenance transforms industrial safety from a cost center focused on compliance into a value driver delivering measurable ROI through reduced maintenance costs, prevented downtime, lower insurance premiums, and protected business continuity. More critically, it saves lives by identifying hazards in their incipient stages—when intervention is straightforward and consequences are minimal.
For Indian industry, this technology arrives at a pivotal moment. As manufacturing expands under Make in India initiatives, as smart cities integrate building safety with urban infrastructure, and as regulatory standards evolve toward intelligent connected systems with NBC 2025, the convergence of AI, IoT, and fire safety addresses genuine needs with proven solutions.
The success of indigenous platforms like NFire—developed through R&D partnerships at IIT Gandhinagar, engineered specifically for Indian environmental conditions, achieving dual compliance with IS/ISO 7240 and EN54 standards, and deployed across critical infrastructure from Indian Railways to banking institutions—demonstrates India’s capacity to not just adopt but lead in this technological evolution. India’s first wireless addressable fire alarm system has evolved into one of the world’s most advanced AIoT fire safety platforms, representing the country’s contribution to global fire safety innovation.
The technology exists. The business case is proven. The regulatory environment increasingly supports it. The only question remaining is: will your facility be among those protected by predictive intelligence, or among those learning its value through painful experience?
The future of fire safety is predictive. The time to act is now.
NFire represents India’s pioneering achievement in wireless addressable AIoT fire alarm systems. Developed through collaboration with IIT Gandhinagar and engineered specifically for Indian conditions, NFire combines 100% wireless addressable technology with predictive AI intelligence, delivering:
To explore how NFire’s AIoT platform can protect your facility with predictive fire safety, contact our team for a consultation and demonstration.
It is a technology-driven approach that uses AI, IoT sensors, and real-time analytics to predict fire risks before ignition occurs.
It detects early warning signs like overheating, gas leaks, and vibration changes—allowing corrective action before a fire starts.
Traditional alarms detect smoke or heat after a fire begins. Predictive systems identify risks days or weeks in advance.
High-risk sectors such as chemical plants, pharma manufacturing, warehouses, oil & gas, and data centers benefit the most.
Yes. Advanced systems comply with IS/ISO 7240 standards and align with upcoming NBC 2025 requirements.
Yes. By analyzing multiple sensor inputs, AI systems can reduce false alarms by up to 90%.
Most facilities achieve ROI within 12–18 months through reduced downtime, maintenance savings, and lower insurance premiums.
Yes. Modern AIoT platforms integrate with BMS, HVAC, and SCADA using protocols like Modbus and BACnet/IP.