India’s smart building revolution is transforming how we protect lives and property from fire emergencies. With the National Building Code (NBC) 2025 mandating addressable fire detection systems for high-rise buildings above 15 meters and the global smart fire detector market projected to reach $3,885.7 million by 2033, facility managers face a critical question: How do we seamlessly integrate intelligent fire safety systems with building management systems (BMS) to create truly smart, safe environments?
This comprehensive guide explores the integration architecture and best practices that are redefining fire safety in India’s commercial buildings, based on international standards, cutting-edge AIoT technology, and real-world implementation experiences.
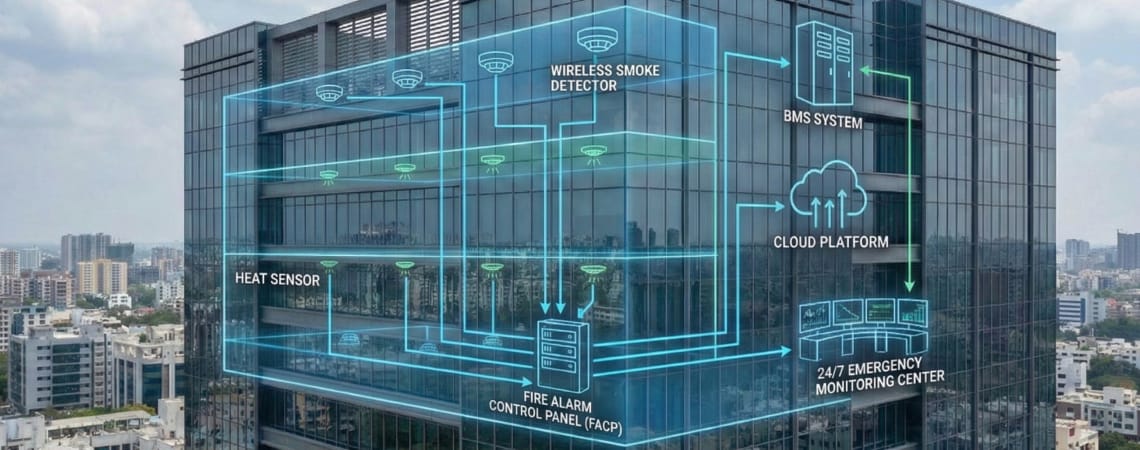
Traditional fire alarm systems operated as standalone safety devices—reactive, isolated, and limited in their ability to communicate with other building systems. Today’s smart buildings demand more: integrated, predictive, and intelligent fire safety ecosystems that work seamlessly with HVAC, access control, lighting, and emergency management systems.
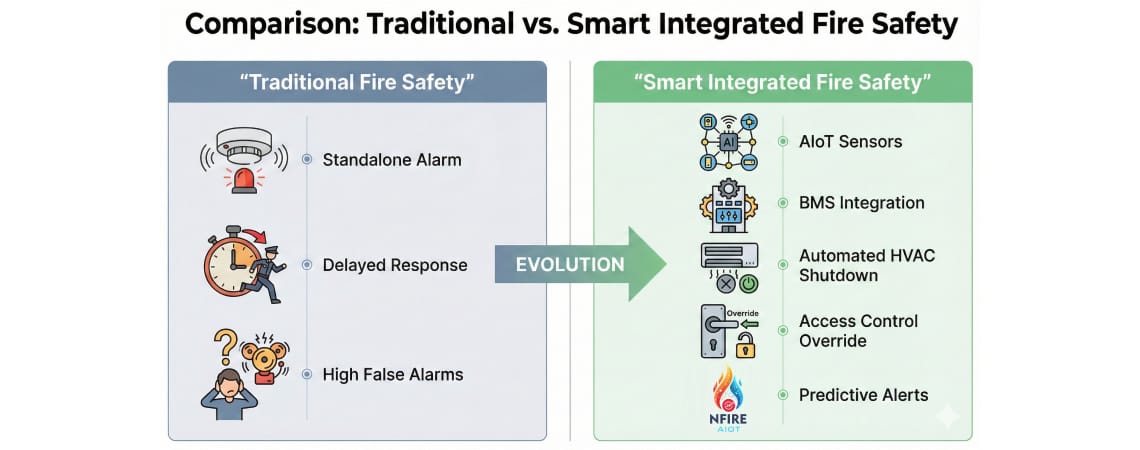
According to research published in Building Management Systems literature, modern BMS integration enables:
Modern smart building fire safety integration follows a four-layer architecture that enables seamless communication and intelligent decision-making:
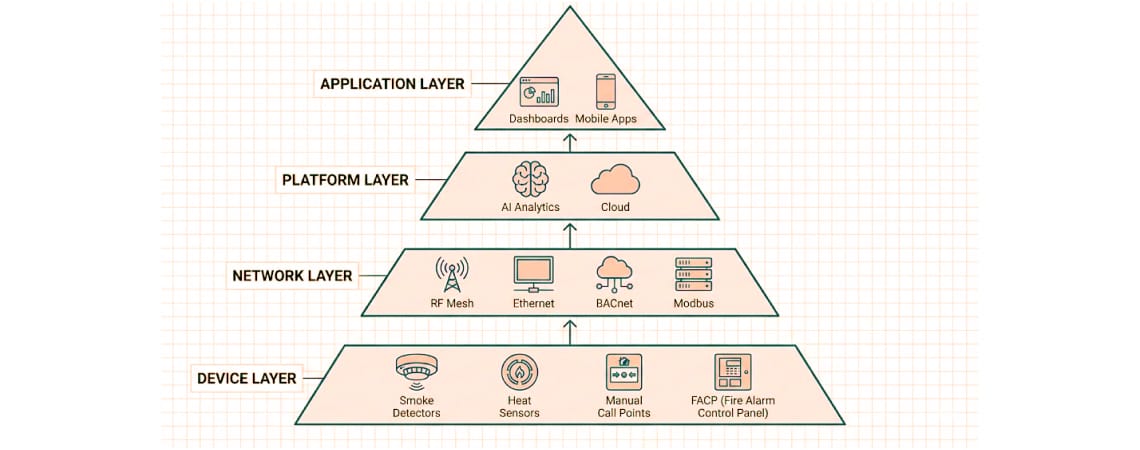
According to ISO 7240-25 standards, wireless addressable systems using radio frequency links must maintain the same reliability and performance criteria as traditional wired systems while offering superior installation flexibility.
Artificial Intelligence combined with the Internet of Things (AIoT) represents the most significant advancement in fire safety technology since the invention of the smoke detector. Research from leading fire safety journals demonstrates how AIoT transforms fire detection from reactive to predictive.
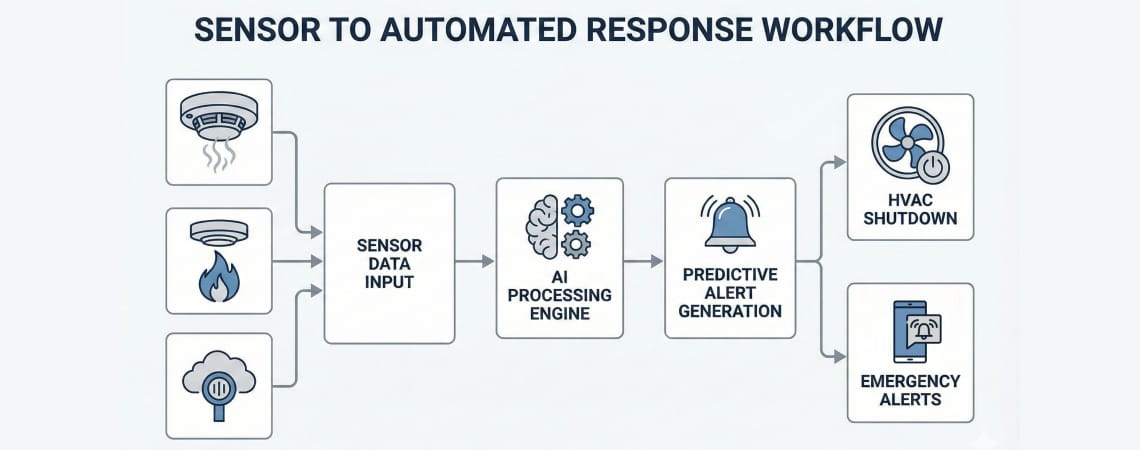
1. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for False Alarm Reduction
Traditional fire detectors rely on single-parameter thresholds that can’t distinguish between actual fire signatures and benign events like steam, dust, or cooking fumes. AIoT systems analyze multiple data streams simultaneously:
According to recent studies on AI-driven fire detection, intelligent multi-sensor fusion can reduce false alarms by over 90% while maintaining 95.7% accuracy in detecting actual fire events.
2. Predictive Fire Risk Assessment
AI algorithms analyze historical data, environmental conditions, usage patterns, and past incidents to create dynamic risk profiles for different building zones. This enables:
3. Super Real-Time Fire Forecasting
Advanced AI models can transform discrete sensor array data into high-dimensional spatiotemporal temperature fields, enabling super real-time fire scene reconstruction. Research from AIoT-powered Digital Twin systems demonstrates this capability can predict fire development and hazardous floor regions faster than actual fire progression—critical for supporting smart firefighting and rescue operations.
Infrastructure Evaluation Before integration begins, conduct a comprehensive assessment:
✓ Identify all fire protection systems to be integrated (sprinklers, alarms, smoke detectors, suppression systems)
✓ Evaluate BMS capabilities for fire alarm monitoring, automation, and real-time alerts
✓ Assess communication protocols used in both systems (BACnet, Modbus, LonWorks, OPC)
✓ Define integration points: FACP, HVAC shutdown, emergency lighting, access control, elevator recall
✓ Review regulatory requirements: NBC Part 4, IS/ISO 7240, state fire safety codes
Design Documentation IS O 7240-14 emphasizes that fire detection and alarm system (FDAS) design must use a systematic and documented process. All assumptions, equipment selection rationale, and site-specific information must be documented for:
Communication Architecture
Establish seamless data exchange between fire protection and BMS:
Fire Alarm Control Panel (FACP) Connection:
HVAC Integration:
Suppression System Monitoring:
Access Control Integration:
Elevator Management:
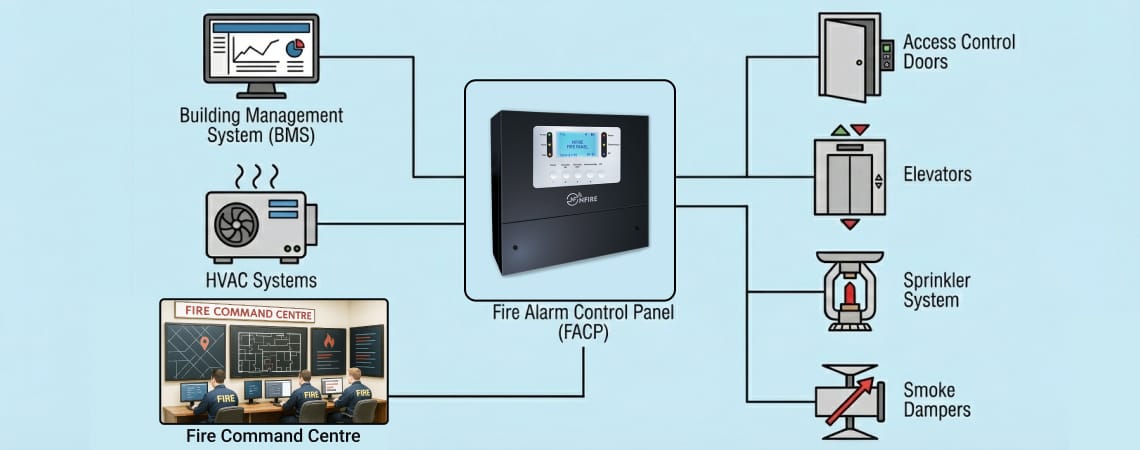
BMS Programming Requirements:
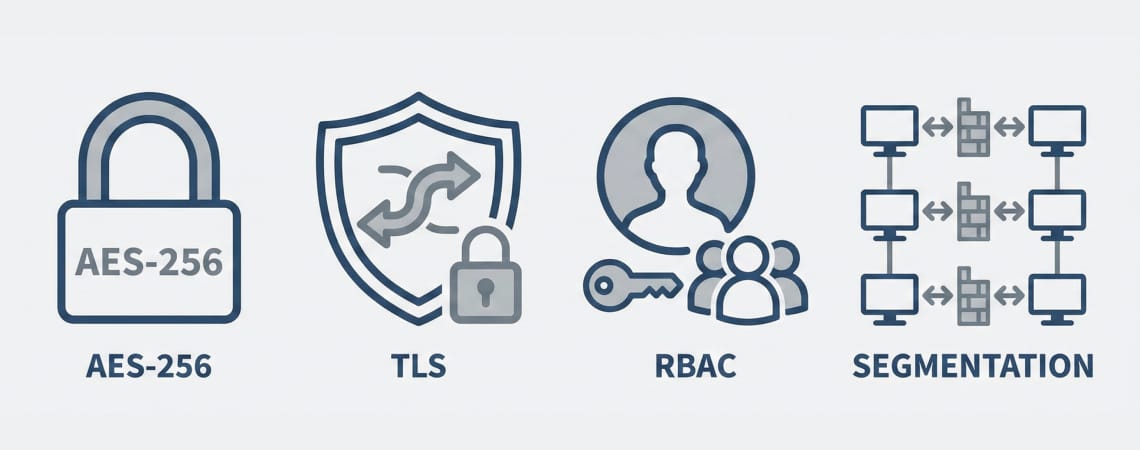
Data Security and Cybersecurity
With interconnected systems, security becomes paramount:
✓ Implement AES-256 encryption for all data transmission
✓ Use TLS 1.3 for secure communication protocols
✓ Establish role-based access control with audit trails
✓ Regular security updates and vulnerability assessments
✓ Network segregation between fire safety and general IT systems
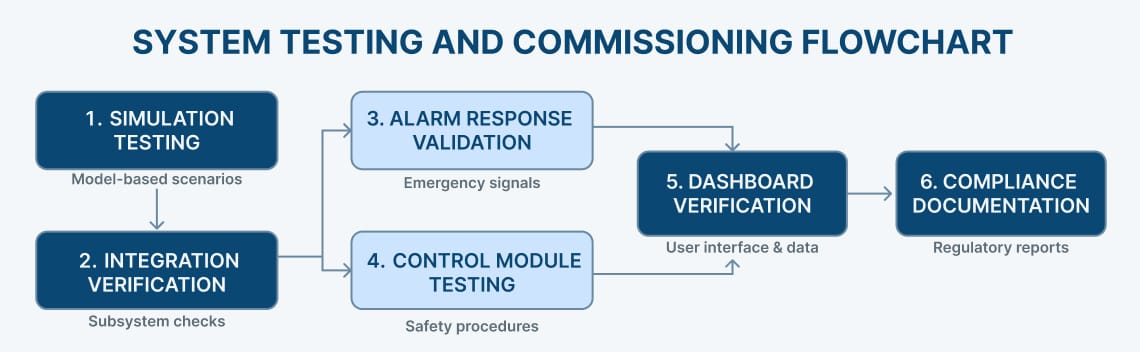
Comprehensive testing validates system reliability before live operation:
Simulation Testing:
Integration Verification:
Compliance Documentation: Document the complete integration architecture including:
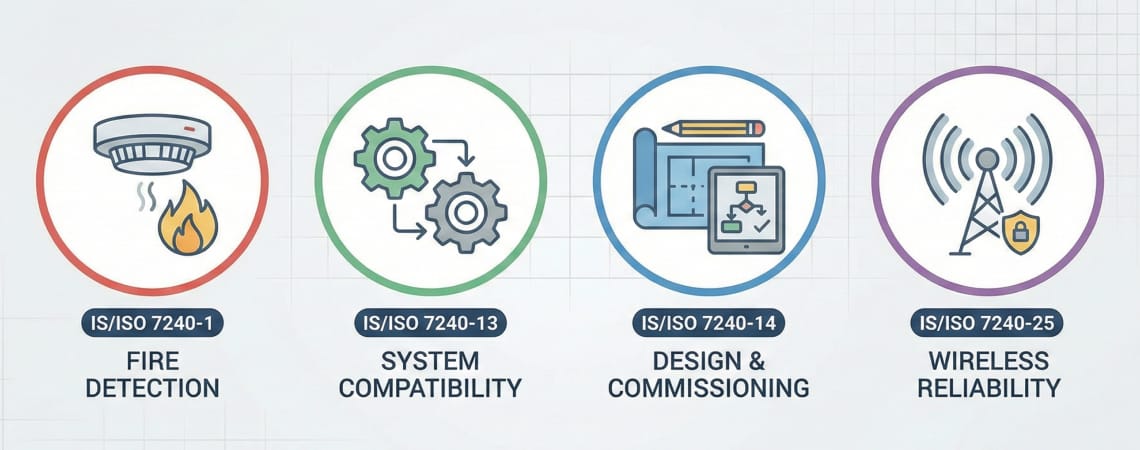
IS/ISO 7240: International Fire Detection and Alarm Standards
The ISO 7240 series, adopted as Indian Standards, provides comprehensive requirements for fire detection and alarm systems:
IS/ISO 7240-1: General Requirements
IS/ISO 7240-13: System Compatibility Critical for integration projects, this part specifies:
IS/ISO 7240-14: Design, Installation, and Commissioning This standard provides the roadmap for integration:
IS/ISO 7240-25: Wireless System Requirements For wireless addressable systems like NFire:
Fewer false alarms mean guests sleep through the night without unnecessary evacuations. When real emergencies occur, precise location information and automated floor-specific announcements guide evacuation efficiently without panic. Smart hotels recognize that visible safety infrastructure—including modern fire detection—signals professionalism and care to increasingly safety-conscious travelers.
The NBC 2025 draft introduces stricter fire safety mandates for Indian buildings:
Addressable Fire Detection Systems: Mandatory in all residential buildings above 15 meters, with:
Smart Alarms and Evacuation Systems:
IoT-Enabled Fire Alarms:
Fire Safety Equipment Requirements: Per NBC Part 4, buildings must have:
IS 2189: Indian Standard for Automatic Electrical Fire Alarm Systems
NBC Part 4: Fire and Life Safety comprehensive requirements
State Fire Service Acts: Local compliance requirements (varies by state)
Fire NOC: Mandatory Fire No Objection Certificate before occupancy
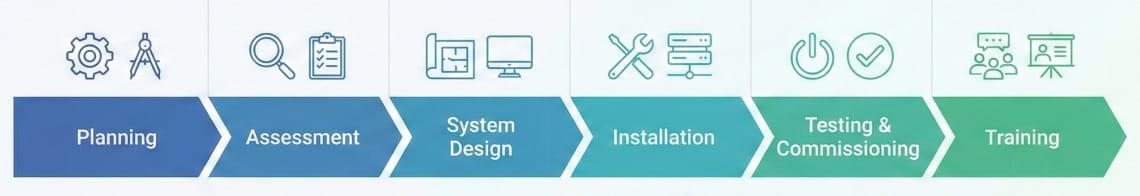
Week 1-2: Stakeholder Alignment
Week 3-4: Technical Assessment
Week 5-8: System Design
Month 3-4: Implementation
Hardware Installation:
Software Configuration:
Month 5: Testing and Commissioning
System Validation:
Month 6: Training and Handover
Operational Readiness:
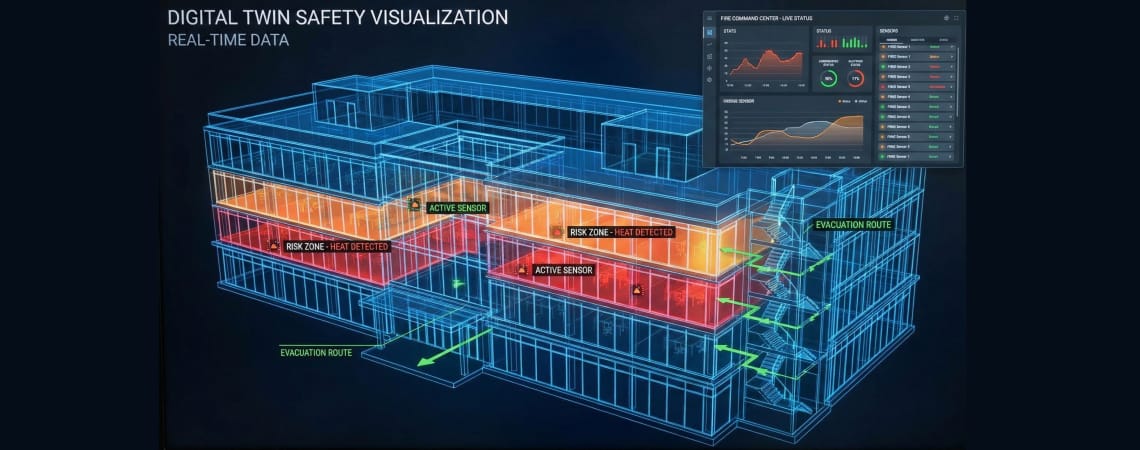
Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical buildings, enabling revolutionary fire safety capabilities:
Real-Time Fire Scene Visualization:
Predictive Analytics:
Training and Preparedness:
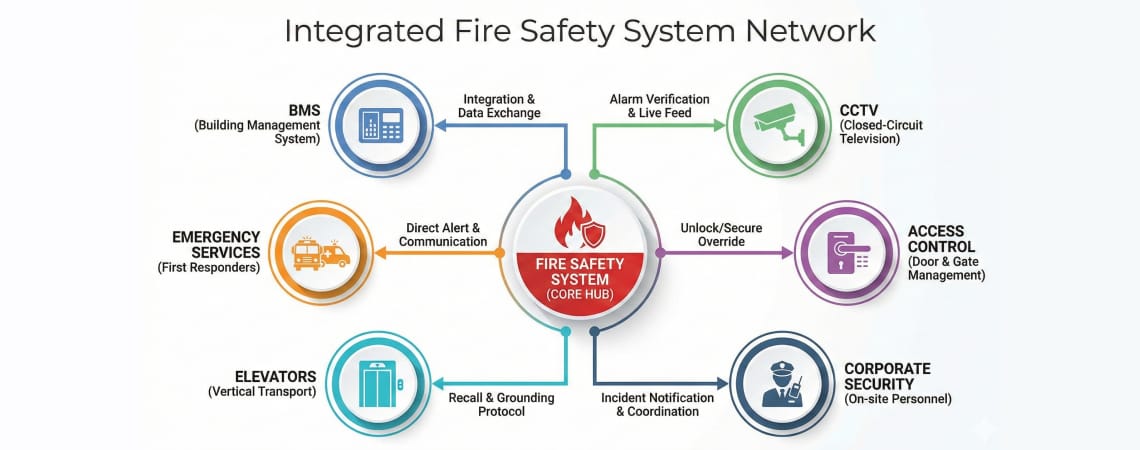
Modern fire safety systems must integrate beyond BMS:
Building Automation Protocols:
Emergency Services Integration:
Corporate Security Systems:
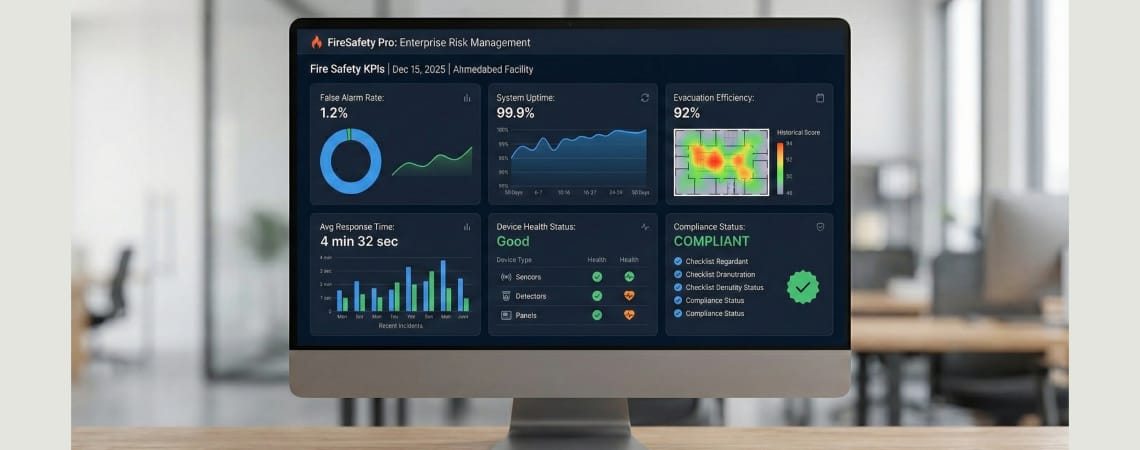
Track these key performance indicators to validate integration effectiveness:
✓ False Alarm Rate: Target <5% with AIoT implementation (traditional systems: 30-50%)
✓ Incident Response Time: From detection to fire service notification (<60 seconds)
✓ System Availability: Uptime >99.9% with redundant communications
✓ Device Health Score: Percentage of devices in optimal operating condition
Safety Outcomes
✓ Evacuation Efficiency: Time to complete building evacuation (measured in drills)
✓ Zero Fire Fatalities: In monitored buildings with integrated systems
✓ Property Loss Reduction: Minimize damage through early detection
✓ Emergency Response Coordination: Seamless multi-system coordination
Compliance and Management
✓ Regulatory Compliance: 100% adherence to IS/ISO 7240 and NBC requirements
✓ Audit Readiness: Complete documentation and test records
✓ Maintenance Efficiency: Predictive alerts reduce reactive repairs by 70%
✓ Energy Savings: HVAC integration reduces unnecessary system operation
Challenge 1: Legacy System Compatibility
Problem: Existing fire systems using proprietary protocols can’t communicate with modern BMS.
Solution:
Challenge 2: Network Security Concerns
Problem: Interconnected systems increase cybersecurity vulnerability.
Solution:
Challenge 3: Data Overload and Analysis Paralysis
Problem: Integrated systems generate vast amounts of data that overwhelm facility teams.
Solution:
Challenge 4: False Alarm Management
Problem: Traditional systems trigger unnecessary evacuations, causing operational disruption.
Solution:
Regular sensor maintenance and sensitivity calibration
Emerging Trends
The integration of intelligent fire safety systems with building management platforms represents more than a technological upgrade—it’s a fundamental shift in how we protect lives and property in India’s rapidly urbanizing landscape.
With NBC 2025 mandating addressable systems for buildings above 15 meters, the time to embrace smart building fire safety integration is now. The benefits are compelling:
✅ Enhanced Safety: Predictive detection, faster response, intelligent evacuation
✅ Operational Efficiency: Reduced false alarms, automated coordination, predictive maintenance
✅ Regulatory Compliance: Meeting IS/ISO 7240, NBC 2025, and state fire safety requirements
✅ Cost Optimization: Lower installation costs with wireless systems, reduced property loss, energy savings
✅ Future-Ready: Scalable architecture supporting emerging technologies
For facility managers, safety officers, and building owners, the question is no longer whether to integrate fire safety with BMS, but how to implement it effectively. By following the integration architecture and best practices outlined in this guide—combined with cutting-edge AIoT technology—you can create truly smart, safe buildings that protect occupants while optimizing operations.
NFire’s AIoT-based wireless addressable fire alarm system delivers the complete smart building integration solution:
✓ 100% Wireless Addressable Technology – Deploy in hours, not weeks
✓ AIoT Intelligence – Predictive alerts, 90% false alarm reduction, real-time analytics
✓ NBC 2025 Compliant – IS/ISO 7240 and EN54 certified
✓ Seamless BMS Integration – BACnet, Modbus, TCP/IP support
✓ Digital Twin Visualization – 2D/3D fire command centers
✓ Made in India – Engineered for Indian conditions, built at IIT Gandhinagar
Contact NFire today for a personalized consultation on transforming your building’s fire safety infrastructure.
Contact NFire today for a personalized consultation on transforming your building’s fire safety infrastructure.
Conventional systems identify fire by zone (e.g., “3rd floor”), while addressable systems pinpoint the exact device location (e.g., “Room 305, southeast corner”). Addressable systems are required by NBC 2025 for buildings above 15 meters and enable precise emergency response.
Wireless addressable systems meeting IS/ISO 7240-25 standards deliver equivalent performance to wired systems while offering significant advantages: faster installation (hours vs. weeks), lower infrastructure costs, easier scalability, and minimal building disruption during deployment.
The primary protocols are BACnet/IP (most common for building automation), Modbus TCP/IP (industrial applications), and standard TCP/IP for cloud integration. Systems should support multiple protocols for flexibility.
AIoT systems analyze multiple sensor inputs simultaneously (smoke, heat, gas, humidity) using machine learning algorithms to distinguish actual fire signatures from benign events like steam or dust. This multi-sensor fusion approach achieves over 90% false alarm reduction compared to traditional single-parameter detection.
NBC 2025 mandates addressable fire detection systems for all residential buildings above 15 meters, smart alarms with evacuation guidance, IoT-enabled systems with automatic emergency service coordination, and comprehensive fire protection equipment based on building height and occupancy.
For new installations, expect 4-6 months from planning to commissioning. Retrofits in occupied buildings may take 6-8 months depending on complexity. Wireless systems significantly reduce installation time compared to wired alternatives.
Bi-annual comprehensive testing (NBC requirement), quarterly sensor checks, monthly system health reviews, and continuous AI-powered predictive maintenance monitoring. Modern systems provide automated alerts for sensor cleaning, battery replacement, and component servicing.
Yes, through protocol converters and field controllers supporting multiple communication standards. However, upgrading to modern wireless addressable systems often provides better long-term value through enhanced capabilities and reduced maintenance.